I. The Importance of the Spleen and Stomach: The Body’s “Granary Official”
In traditional Chinese medicine, the spleen and stomach are referred to as the “granary official, from which the five flavors emerge,” meaning they act like the body’s warehouse and logistics hub, responsible for receiving, digesting, and distributing nutrients from food, playing a crucial role in maintaining health.
1. The Relationship Between the Spleen and Stomach and Diseases:
- Whether adults or children, the function of the spleen and stomach must be considered in the treatment process of traditional Chinese medicine. For example, in pediatric massage, most treatments focus on regulating the spleen and stomach because their function directly affects a child’s growth and development and immunity. Issues such as coughing, wanting to grow taller, adenoid hypertrophy, rhinitis, and low immunity can all be improved by regulating the spleen and stomach.

2. How to Assess the Health of the Spleen and Stomach:
- By observing a child’s eating, drinking, bowel movements, and sleep, one can understand the absorption and transformation capabilities of the spleen and stomach:
- Diet: Whether the appetite is normal, and if there is picky or selective eating.
- Digestion: Whether there are symptoms such as bloating, food retention, or vomiting.
- Bowel Movements: Whether the stools are regular, and if there are issues like constipation or diarrhea.
- Mental State: Whether there are signs of fatigue, drowsiness, or lack of concentration.
II. Common Misconceptions in Regulation: Understanding Types of Spleen Deficiency
Many people do not clearly distinguish between spleen qi deficiency, spleen yang deficiency, and spleen yin deficiency, leading to improper regulation and worsening of the condition.
1. Spleen Qi Deficiency:
- Symptoms: Easily bloated after eating; fatigue, unwillingness to move; loss of appetite.
- Regulation Direction: Strengthening the spleen and benefiting qi.
2. Spleen Yang Deficiency:
- Symptoms: Abdomen and hands and feet easily feel cold; frequent diarrhea.
- Regulation Direction: Warming and supplementing spleen yang (such as moxibustion: suitable for people with spleen yang deficiency because moxibustion can warm and supplement yang qi, promoting the flow of yang qi).
3. Spleen Yin Deficiency:
- Symptoms (common in children): Dry lips and nose; sore throat, wanting to drink water but not actively doing so;
- Regulation Direction: Nourishing yin and clearing heat.
III. Good Methods for Daily Regulation of the Spleen and Stomach
1. Moxibustion: Warming and Supplementing Spleen Yang
Target Audience: People with spleen yang deficiency.
Common Acupoints:
- Shenque Point (navel):
- It is a channel that connects with the body’s innate qi, making it easy to absorb. Suitable for symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhea caused by cold. Method of operation: Can use salt-separated moxibustion or ginger-separated moxibustion. Adults: Moxibustion for about ten minutes with three sticks each time. Children: Moxibustion for five minutes each time, avoiding prolonged sessions.
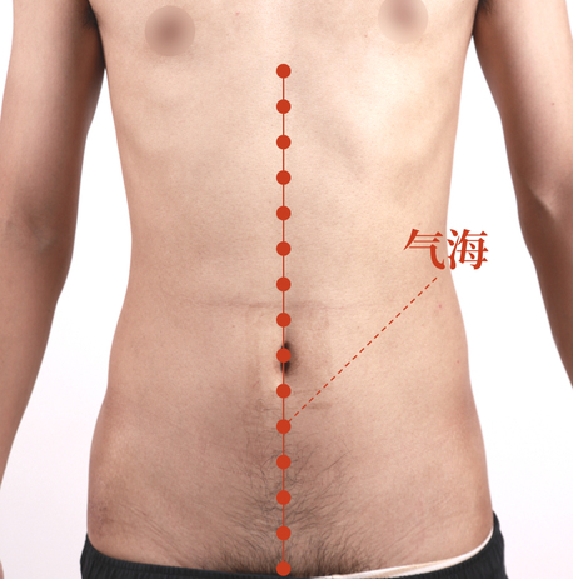
- Qihai Point (1.5 inches below the navel):
- It is the “ocean of qi,” stimulating this point can promote the transformation and absorption of the spleen and stomach. Method of operation: Can use moxibustion or clockwise massage.
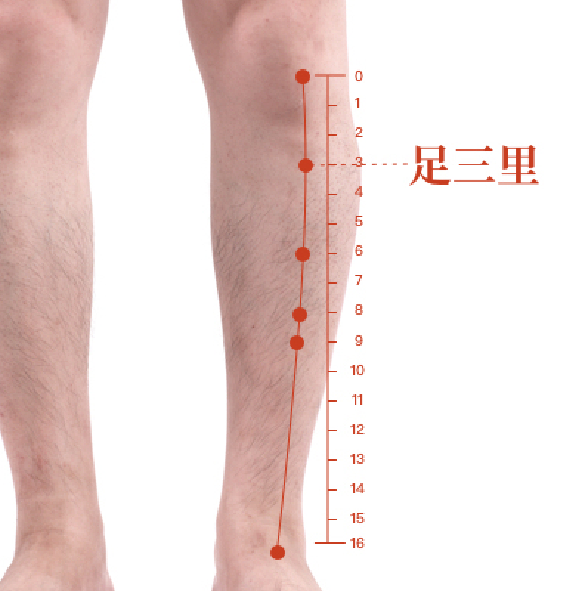
- Stomach 36 Point (located on the front of the lower leg):
- It is a key health acupoint that can enhance spleen and stomach function. Method of operation: Can use moxibustion or massage.
Precautions: Using coarse salt is more effective. To prevent burns, portable moxibustion or special moxibustion jars can be used. Portable moxibustion is safer for children. Control the heat to avoid causing internal heat.
2. Dietary Regulation: Nourishing Yin and Clearing Heat
Target Audience: Children with spleen yin deficiency.
Recommended Foods: Lotus root: Can be eaten raw or cooked, has the effect of clearing heat and generating fluids. Yam: Can strengthen the spleen and benefit qi, nourish yin and moisten dryness. Lily: Can moisten the lungs and stop coughing, calm the mind. Kudzu root: Can generate fluids and quench thirst, raise yang and stop diarrhea. Aloe vera: Can clear heat and detoxify, moisten the intestines and promote bowel movements.
Dietary Recommendations: Avoid spicy and greasy foods to prevent exacerbating internal heat. Control the intake of cold drinks and cold foods.

3. Massage and Tui Na: Strengthening the Spleen and Assisting Digestion
Target Audience: All people.
Common Techniques:
- Clockwise abdominal massage: Can promote intestinal peristalsis and relieve bloating. Method of operation: With the navel as the center, massage in a clockwise direction. Massage for 20-30 minutes each time, can be done in segments.
- Tapping the spleen meridian: Can unblock the spleen meridian and promote the flow of qi and blood. Method of operation: Gently tap the spleen meridian on the inner side of the lower and upper legs with a mugwort hammer.
- Massaging the Banmen Point: The Banmen Point is located on the palm’s thenar eminence and has a good regulatory effect on the spleen and stomach. Method of operation: Press and rub with the thumb for 3-5 minutes each time.
Precautions:
- Massage time: More effective during the day, but can also be done at night. Massage intensity: Moderate is sufficient, avoid excessive force.
4. Other Recommendations:
- Avoid overeating: Encourage small, frequent meals to reduce the burden on the spleen and stomach. Eat fewer processed foods: Choose natural, unprocessed foods. Increase exercise: Appropriate exercise can promote digestion and enhance physical fitness. Ensure adequate sleep: Sleep is an important part of body repair and recovery.
IV. Case Analysis: Regulation of a Child with Spleen Yin Deficiency
Case Description: A 5-year-old boy often feels dry mouth, dry throat, constipation, likes cold drinks, and has a red tongue with yellow coating.
Traditional Chinese Medicine Analysis: Symptoms indicate spleen yin deficiency with internal heat.
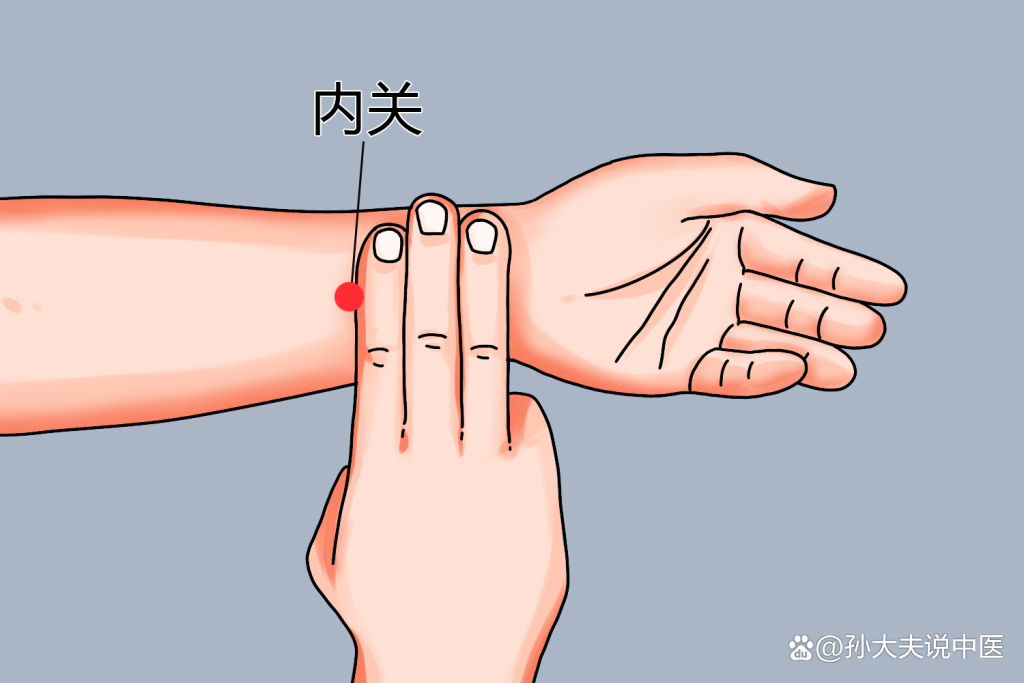
Regulation Plan: Dietary adjustments: ① Eat more foods that nourish yin and moisten dryness, such as pears, apples, honey, etc. ② Avoid spicy and greasy foods. Chinese medicine regulation: Take Chinese medicine formulas containing ingredients like American ginseng to nourish yin and clear heat. Massage: Massage the Neiguan and Sanyinjiao points daily to improve digestion and alleviate symptoms. After two weeks of regulation, the boy’s symptoms significantly improved, with relief from dry mouth and throat, and the disappearance of constipation.
V. Conclusion
By understanding the importance of the spleen and stomach, distinguishing between different types of spleen deficiency, and adopting appropriate regulation methods, one can effectively improve spleen and stomach function and promote overall health. Whether adults or children, good spleen and stomach health can be maintained through daily diet, lifestyle habits, and traditional Chinese medicine regulation methods, leading to a healthy life.


Leave a Reply